In today’s fast-paced manufacturing world, injection molding stands out as a pivotal process that shapes the products we use daily. From the sleek casing of your smartphone to the durable dashboard of your car, injection molding plays a crucial role in bringing innovative designs to life. This comprehensive guide delves into the intricacies of injection molding, exploring its principles, the complete process, and its vast applications across various industries. Whether you’re a seasoned professional or a curious newcomer, join us as we uncover the art and science behind this transformative technology, and discover how it drives product design, development, and prototyping in the modern era.
What is Injection Molding?
In today’s fast-paced manufacturing world, injection molding stands out as a pivotal process that shapes the products we use daily. From the sleek casing of your smartphone to the durable dashboard of your car, injection molding plays a crucial role in bringing innovative designs to life. This comprehensive guide delves into the intricacies of injection molding, exploring its principles, the complete process, and its vast applications across various industries. Whether you’re a seasoned professional or a curious newcomer, join us as we uncover the art and science behind this transformative technology, and discover how it drives product design, development, and prototyping in the modern era.
How Injection Molding Works
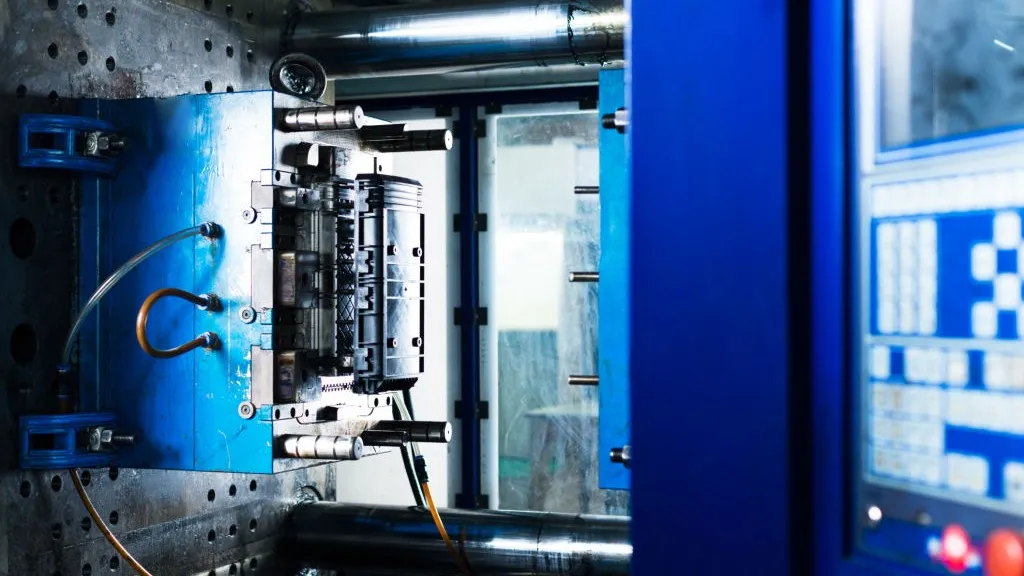
The basic principle of injection molding is to use an injection molding machine to heat the plastic material to a molten state and then inject it into the mold through a screw or plunger. The mold usually consists of two parts, forming the front and back of the product respectively. The plastic cools and solidifies in the mold, and the product is ejected after the mold is opened.
Injection molding machines mainly consist of the following parts:
- Hopper: used to store and convey plastic pellets.
- Heating barrel: heats the plastic pellets to a molten state.
- Screw: pushes the molten plastic into the mold.
- Mold: determines the shape and size of the product.
The Complete Process of Injection Molding
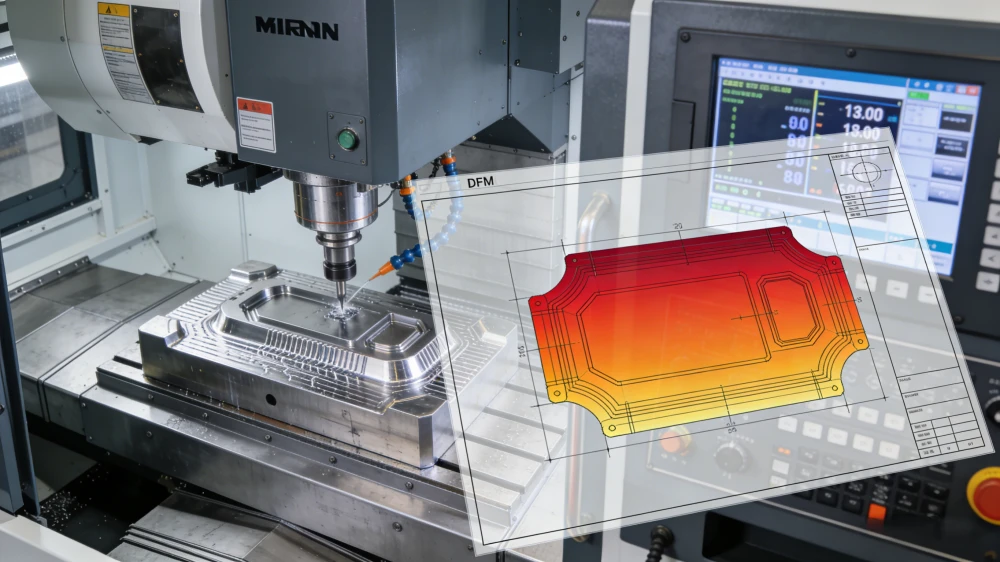
Injection Mold Making
Product Design and Mold Design
Product Design: First, the product design is carried out according to customer needs or market needs to determine the size, shape, and function of the product. This stage is crucial in the product design and development cycle, as it lays the groundwork for successful prototyping and manufacturing.
Mold Design: Based on the product design, engineers use computer-aided design (CAD) software to design the mold. Mold design needs to consider the product’s demolding angle, gate location, cooling system, and ejection mechanism, etc.
Mold Manufacturing
Material Selection: Molds are usually made of high-strength metal materials such as steel or aluminum. Steel molds are highly durable and suitable for mass production, while aluminum molds are more suitable for small batch production and rapid prototyping.
Processing Technology:
- Milling and Turning: Use CNC machine tools for preliminary processing to form the basic shape of the mold.
- Electrical Discharge Machining (EDM): Used to process complex mold details and precision parts.
- Grinding and Polishing: Grind and polish the mold surface to improve the surface finish and ensure the appearance quality of the product.
- Cooling System: Design and install cooling channels in the mold to quickly cool the plastic during the molding process.
- Assembly and Debugging: Assemble the various parts of the mold together and debug them to ensure that the functions of the mold are normal.
Mold Testing and Optimization
Mold Trial: Before actual production, mold trial is carried out to test the performance of the mold and product quality. The mold trial stage may find areas that need adjustment.
Optimization Adjustment: According to the mold trial results, the mold is adjusted and optimized as necessary to ensure that the product meets the design requirements.
Injection Molding
Material Preparation
- Material Selection: Select appropriate plastic materials such as polypropylene (PP), polyethylene (PE), polystyrene (PS), etc., according to the needs of the product.
- Drying Treatment: Dry the plastic material to remove moisture and avoid bubbles or other defects in the finished product.
Plastic Melting
- Hopper Feeding: Plastic particles are added to the hopper of the injection molding machine. The hopper is responsible for feeding the particles into the heating barrel.
- Heating Barrel Heating: After the plastic particles enter the heating barrel, the heater in the barrel heats them to a molten state. Temperature control is very important to ensure that the plastic is evenly melted.
Injection
- Screw Push: The screw or plunger in the heating barrel pushes the molten plastic through the nozzle into the mold cavity.
- Injection Control: Injection speed and pressure need to be precisely controlled to ensure that the plastic completely fills every corner of the mold and avoids gaps or incomplete parts.
Holding Pressure
Pressure Holding: After the plastic fills the mold, pressure continues to be applied for a period of time. This is to compensate for the shrinkage of the plastic when it cools and ensure the density and dimensional accuracy of the product.
Holding Time: Depending on the complexity and material properties of the product, the holding time will vary.
Cooling
Solidification Molding: The plastic cools and solidifies in the mold to form the final shape of the product. The cooling time depends on the thermal conductivity of the material, the thickness of the product, and the temperature of the mold.
Mold Design: The mold usually has cooling channels to accelerate the cooling process by circulating coolant.
Mold Opening
Mold Separation: After cooling is completed, the mold opens and the product is ejected. The ejection system design ensures that the product will not be deformed or damaged.
Ejection System: Includes ejector pins or ejector plates to help push the product out of the mold.
Post-Processing
- Removing Flash: After injection molding, the product may have excess plastic edges (flash) that need to be removed manually or automatically.
- Surface Treatment: Depending on the product requirements, grinding, spraying, or other surface treatment may be required.
Quality Inspection
Inspection Standards: Check the size, appearance, and function of the product to ensure that it meets the design specifications and quality standards.
Inspection Tools: Use measuring tools and inspection equipment for quality control.
Packaging and Transportation
Packaging: Qualified products are properly packaged to protect their integrity during transportation.
Labeling and Transportation: Clearly mark product information and prepare for transportation to customers.
Application Areas of Injection Molding
1. Application Cases in Different Industries
Automotive Industry: Injection molding is widely used in the automotive industry to produce various plastic parts such as bumpers, dashboards, door panels, and headlight housings. These parts need to have high strength, durability, and precise dimensions to ensure the safety and performance of the vehicle.
Electronics Industry: Electronic products require lightweight, durable, and beautiful housings, and injection molding can meet these requirements. Common applications include mobile phone housings, TV housings, computer keyboards, and mice, etc.
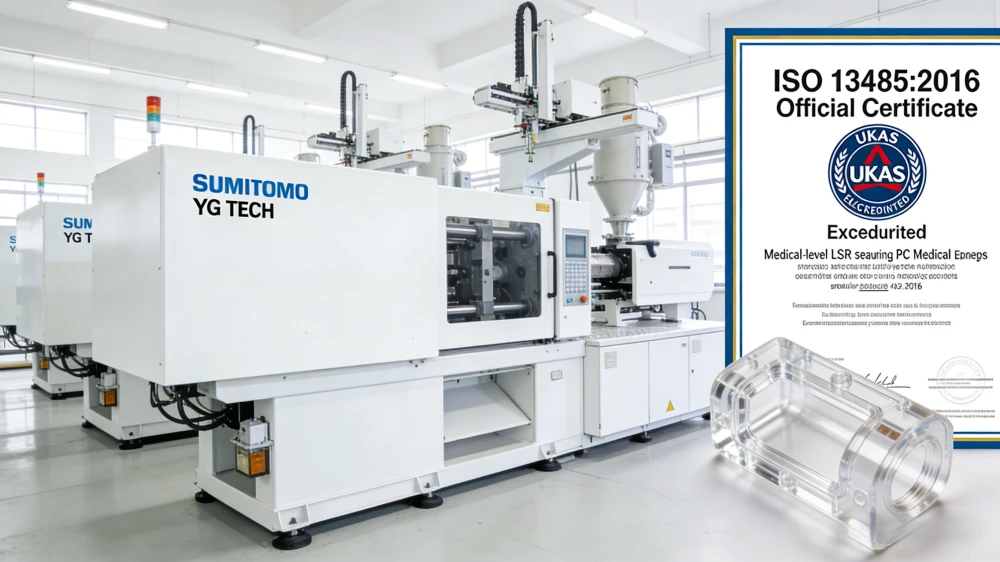
Medical Industry: In the medical industry, injection molding is used to manufacture disposable syringes, pharmaceutical packaging, medical device housings, and other precision plastic parts. Since medical products have extremely high requirements for hygiene and precision, the repeatability and clean production capabilities of injection molding are very important.
Consumer Goods Industry: From kitchen utensils to children’s toys, injection molding is ubiquitous in the consumer goods industry. Its low cost and high efficiency make it an ideal choice for producing large quantities of consumer goods.
2. Typical Product Examples
- Auto Parts: such as door handles, dashboard components, air conditioning vents, etc.
- Electronic Product Housings: such as smartphone housings, tablet computer cases, headphone housings.
- Household Items: such as plastic chairs, storage boxes, flower pots.
- Industrial Components: such as gears, valves, pipe joints.
Future Trends in Injection Molding
1. Development of New Materials and New Technologies
New Material Development: With the advancement of science and technology, more and more high-performance plastic materials have been developed, such as high-temperature resistant plastics, impact-resistant plastics, and biodegradable plastics. These materials have expanded the application range of injection molding.
Smart Manufacturing Technology: Injection molding is being combined with the Internet of Things (IoT) and artificial intelligence (AI) to automate and intelligentize the production process. These technologies can improve production efficiency, reduce waste, and provide real-time quality monitoring.
Additive Manufacturing Combination: 3D printing technology combined with injection molding can achieve rapid prototyping in the product development stage and shorten the time to market.
2. Application of Sustainable Development and Environmentally Friendly Materials
Use of Environmentally Friendly Materials: More and more companies are beginning to use renewable and degradable plastic materials to reduce the impact on the environment.
Closed-Loop Recycling System: Some companies are developing closed-loop recycling systems to recycle and reuse waste plastic products to promote the development of a circular economy.
Energy-Saving Production Technology: By improving injection molding equipment and processes, energy consumption can be reduced, production efficiency can be improved, and carbon emissions can be reduced.
FAQ
1. Common Misunderstandings about Injection Molding
Misunderstanding: Injection molding can only be used for mass production. Although injection molding is more cost-effective in mass production, small-batch production has also become more feasible with the development of rapid mold manufacturing technology.
Myth: All plastics can be injection molded. Not all plastics are suitable for injection molding, and some high-viscosity or heat-sensitive materials may require special handling or other molding processes.
2. Answers to Questions that Readers May Be Concerned About
Q: How long is the production cycle of injection molding?
A: The production cycle depends on the complexity, size, and material of the product. Generally speaking, it ranges from a few seconds to a few minutes.Q: How to choose the right injection molding material?
A: When selecting materials, you need to consider the functional requirements, environmental conditions, cost, and processing characteristics of the product.Q: Is the mold cost high for injection molding?
A: Mold costs are generally high, especially for complex molds, but mold costs can be amortized through large-scale production.
Additional Resources
1. Recommended Books, Articles, or Videos
- “Plastic Injection Molding Technology” – Detailed introduction to the theory and practice of injection molding.
- Online courses: There are many professional courses on injection molding on Coursera and edX.
2. Related Industry Websites or Forums
- Society of Plastics Engineers (SPE): Provides the latest research and industry trends on plastics engineering.
- Injection Molding Forum: An online community for injection molding professionals and enthusiasts to exchange experiences and insights.
- Wikipedia: Injection Molding – Injection Molding – Wikipedia – Provides a comprehensive overview of injection molding, including history, processes, and applications.
These resources provide you with in-depth knowledge of all aspects of injection molding, from the basics to the latest technology trends. Whether you are new to the industry or an experienced professional, this information will provide you with strong support for your career development. Continue to explore the world of injection molding for more valuable insights and knowledge. If you have any questions or thoughts about the injection molding process, please contact us.



